Table of Contents
▲- Inverter Basics Explained
- What to Consider Before Buying an Inverter
- Different Types of Inverters and Their Uses
- How to Calculate Load Requirements
- Choosing the Right Battery for Your Inverter
- Top Inverter Brands and Models
- Installation and Maintenance Tips
- Integrating Solar Power with Your Inverter
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Making Your Final Decision
Power blackouts can upset your daily life, affecting everything from basic comfort to critical work-from-home setups. Finding the best inverter for home use becomes essential for maintaining continuous electricity supply during these unexpected blackouts. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about how to choose the best inverters for home or selecting the perfect inverter that matches your specific power needs, verifying you make an informed decision for your home’s standby power needs.
Inverter Basics Explained
An inverter is a device that converts direct current (DC) power from batteries into alternating current (AC) power that runs most home appliances. During a power blackout, the inverter draws energy stored in batteries and transforms it into usable electricity for your home. Think of it as an interpreter that converts the language of stored energy (DC) into the language your appliances understand (AC).
How Inverters Work
When grid power fails, the inverter automatically detects the blackout and begins converting the DC power from your batteries. This happens through a series of electronic components that quickly switch the direction of the current, creating an switching pattern that imitates the standard household electricity. The quality of this conversion directly outcomes how well your appliances will function during a power failure.
Types of Inverters
| Inverter Type | Description | Best For |
| Pure Sine Wave | Produces clean, smooth power identical to grid electricity | Sensitive electronics, medical machinery, all appliances |
| Modified Sine Wave | Produces stepped waveform that approximates sine wave | Basic appliances, lights, fans, non-sensitive electronics |
| Square Wave | Produces basic square waveform with notable frequencies | Simple tools, basic lighting only |
For most home applications, a pure sine wave inverter is recommended as it provides the cleanest power that’s consistent with all modern electronics. While more expensive at first, pure sine wave inverters protect your valuable devices and ensure they operate efficiently without disturbance or damage.
What to Consider Before Buying an Inverter

Power Capacity and Load Requirements
The most important factor in choosing the best inverter for home use is understanding your power requirements. An inverter that’s too small won’t support all your vital appliances, while one that’s too large is an unnecessary expense. You’ll need to calculate the total energy output of all devices you plan to run concurrently during a power blackout.
Important: Remember that some appliances like refrigerators and air conditioners require a higher “spike power” when starting up—often 2-3 times their running total energy. Your inverter must handle these spike requirements.
Battery Compatibility and Runtime
Your inverter battery blend determines how long you’ll have backup power. Batteries are rated in Ampere-hours (Ah), and the higher this rating, the longer your runtime. For home inverters, tubular batteries are popular due to their longer lifespan and better performance during prolonged electricity failure.
Efficiency and Power Factor
Inverter effectiveness suggests how much of the battery power actually gets converted to usable AC power. Higher efficiency means less energy waste and longer backup times. Look for inverters with efficiency ratings above 90% for maximum performance. The power factor (typically 0.7 for home inverters) helps convert between watts and VA ratings.
Warranty and After-Sales Support
A good warranty reflects the assembler’s confidence in their product. For home inverters, look for at least 2-3 years of warranty scope. Additionally, check the availability of service centers in your area for prompt support when needed.
Need Expert Advice?
Still unsure about which inverter requirements match your home’s needs? Solar power experts can help you calculate the perfect size.
Different Types of Inverters and Their Uses
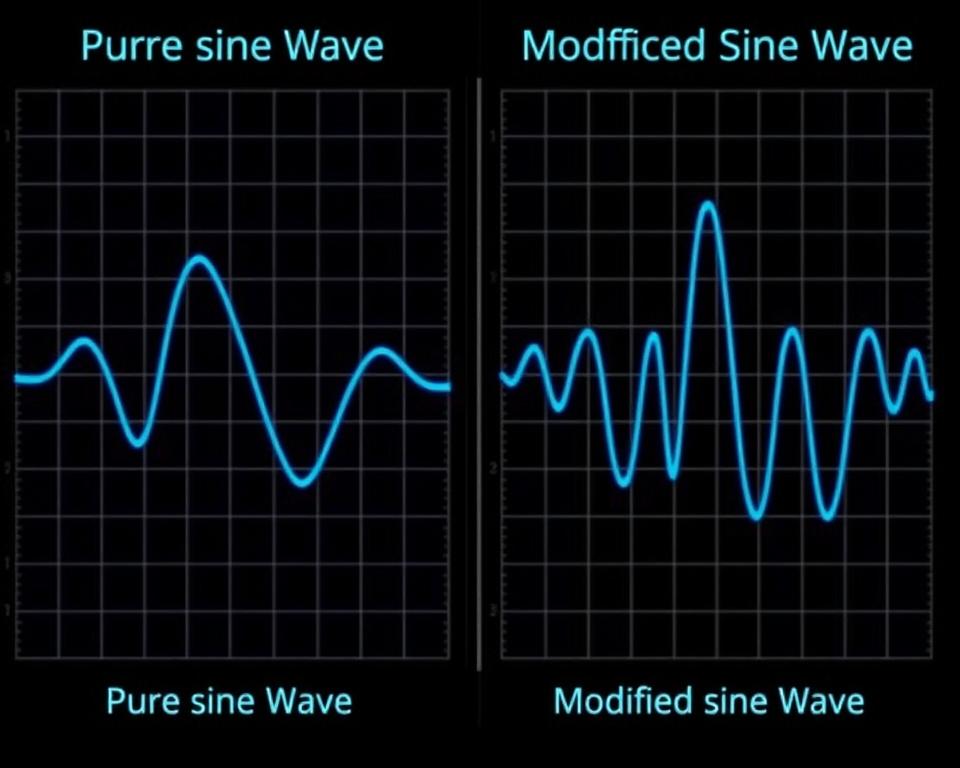
Sine Wave vs. Modified Sine Wave Inverters
The waveform quality is one of the most important variations between inverter types. Pure sine wave inverters produce electricity identical to what comes from your utility company, with smooth, continuous voltage transitions. Modified sine wave inverters produce a stepped waveform that estimates a sine wave but isn’t as smooth.
Pure Sine Wave Advantages
- Adaptable with all electronic devices
- Runs sensitive machinery safely
- Reduces noise in audio equipment
- Extends the lifetime of connected devices
- More productive operation with less heat
Modified Sine Wave Limitations
- May damage sensitive electronics
- Creates vibrating noise in audio machinery
- Causes heating in motors and transformers
- Inconsistent with certain medical devices
- Reduced efficiency in appliances
Solar Hybrid Inverters
A solar hybrid inverter combines traditional inverter functionality with the ability to leverage solar energy. These systems can charge batteries using solar panels during daylight hours and provide backup power during blackouts. For environmentally perceptive homeowners, a solar hybrid inverter offers long-term savings and reduced carbon signature.
Inverter/Charger Combinations
Inverter/charger units not only convert DC to AC but also include a built-in battery charger. When utility power is available, they spontaneously recharge the batteries while coincidently powering your home. During power failure, they effortlessly switch to battery power. This two-way functionality makes them ideal for areas with regular but short power failure.
Which Inverter Type Is Right For You?
If you run sensitive electronics like computers, medical equipment, or modern appliances, a pure sine wave inverter is your best choice regardless of the higher cost.
For basic backup of lights, fans, and non-sensitive devices, a modified sine wave inverter may be enough at a lower price point.
If you’re looking to merge renewable energy, consider a solar hybrid inverter for long-term savings.
How to Calculate Load Requirements
Precisely calculating your power needs is vital for selecting the right inverter capacity. Follow these steps to determine your home’s power needs:
Step 1: List All Essential Appliances
Start by listing all devices you need to run during a power blackout. Typically, this includes lights, fans, refrigerator, television, and perhaps a computer or router. For each appliance, note both its running electricity and starting wattage (if applicable).
Step 2: Calculate Total Running Wattage
| Appliance | Quantity | Running Watts | Total Watts |
| LED Lights | 5 | 10W | 50W |
| Ceiling Fans | 3 | 75W | 225W |
| Refrigerator | 1 | 150W | 150W |
| Television (32″) | 1 | 60W | 60W |
| Router/Modem | 1 | 15W | 15W |
| Total Running Wattage | 500W | ||
Step 3: Account for Starting Surge
Some appliances like refrigerators require a higher starting wattage. For our example refrigerator, the starting surge might be 450W (3x running watts). Ensure your inverter can handle the highest possible spike when multiple devices start concurrently.
Step 4: Convert Watts to VA
Inverters are typically rated in VA (Volt-Amperes). To convert watts to VA, divide by the power factor (usually 0.7 for home inverters):
VA Rating = Total Watts ÷ Power Factor
Example: 500W ÷ 0.7 = 714 VA
For safety, add 20% buffer: 714 VA × 1.2 = 857 VA
Therefore, you should look for an inverter rated at least 900 VA or 1000 VA.
Special Case: Running Air Conditioners
If you need to run a 1.5 ton AC (approximately 1800W) on an inverter, you’ll need a much larger system. The best inverter for 1.5 ton AC would need to handle around 2700 VA plus additionalcapability for other appliances. These specialized inverters often require expert installation and multiple batteries.
Calculate Your Exact Power Needs
Use our free load calculator tool to determine the precise inverter capacity for your specific appliances.
Choosing the Right Battery for Your Inverter

Types of Inverter Batteries
The battery is the heart of your inverter system, determining how long you’ll have power during a power failure. Selecting the right home inverter with battery requires understanding the different battery types and their traits.
Flat Plate Batteries
- Lower initial cost
- Good for areas with irregular power failure
- 2-3 year lifespan
- Requires regular servicing
Tubular Batteries
- Longer lifetime (5-7 years)
- Better for frequent, longer blackouts
- Higher capability preservation
- Requires preodic maintenance
Maintenance-Free Batteries
- No water topping required
- Sealed construction
- Safe for indoor placement
- Higher cost but longer life
Calculating Battery Capacity
Battery capacity is measured in Ampere-hours (Ah). To calculate the battery size you need:
Battery Capacity (Ah) = (Inverter VA × Backup Hours) ÷ Battery Voltage
For example, if you need a 1000 VA inverter to provide 3 hours of backup with a 12V battery:
Battery Capacity = (1000 × 3) ÷ 12 = 250 Ah
For most home applications, tubular batteries offer the best balance of cost, performance, and lifespan. If you’re setting up an inverter for power backup in areas with frequent outages, investing in a high-quality tubular battery is recommended.
Important: Always match your battery voltage with your inverter’s input voltage requirements. Most home inverters work with 12V or 24V battery systems.
Top Inverter Brands and Models

When shopping for the best inverter for home use, considering trustworthy brands can ensure consistency and after-sales support. Here’s a look at some of the top inverter brands and their standout models:
- Known for reliability and service network
- Zelio+ series offers pure sine wave output
- Eco Volt series for budget-conscious buyers
- Smart inverters with LCD displays
- 5-year warranty on select models
- Excellent value for money
- UPS series for computers and sensitive electronics
- Digital display for battery status
- High surge capacity for motor loads
- Wide service network across the country
- Known for battery expertise
- Integrated inverter-battery solutions
- Long battery life with advanced charging
- GQP series for premium performance
- Low maintenance requirements
Best Inverters for Different Home Sizes
| Home Size | Recommended Capacity | Suggested Models | Price Range |
| Small (1-2 rooms) | 600-800 VA | Luminous Eco Volt, Microtek EB Series | $100-150 |
| Medium (2-3 rooms) | 900-1500 VA | Luminous Zelio+, Exide GQP | $150-250 |
| Large (3+ rooms) | 2000+ VA | Microtek UPS EB Series, V-Guard Smart Pro | $250-400 |
| With AC support | 3500+ VA | Su-Kam Falcon+, Luminous Cruze | $400-700 |
Featured: Best Overall Home Inverter
The Luminous Zelio+ 1100 regularly ranks as the best inverter for home use due to its reliable performance, pure sine wave output, and excellent battery charging technology. With a capacity of 1100VA, it can power most vital appliances in a medium-sized home for 3-5 hours depending on the battery capability.
Key features include adaptive battery charging, excess protection, and a digital display for monitoring system status. The Zelio+ series also offers one of the best warranties in the industry.
Installation and Maintenance Tips
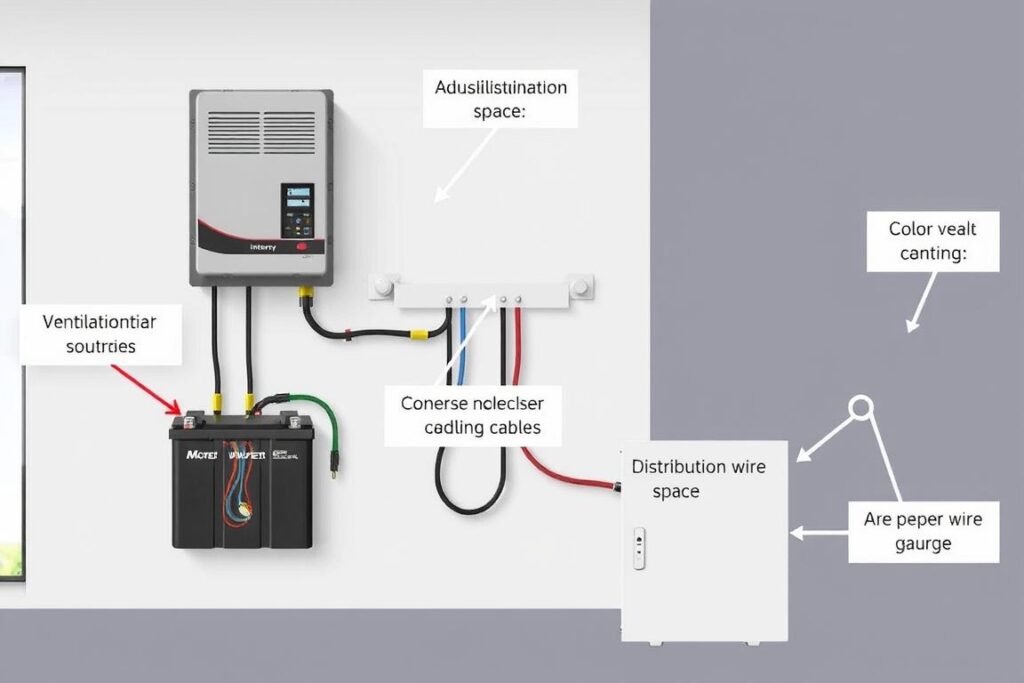
Proper installation and regular maintenance are vital for assuring the durability and optimal performance of your inverter system. Here are some important tips:
Installation Best Practices
- Location: Install your inverter in a well-aired area away from direct sunlight and moisture. Assure at least 6 inches of clearance on all sides for proper air rotation.
- Wiring: Use the correct gauge wire based on your inverter’s capacity. Thicker wires (lower gauge numbers) are needed for higher capacity inverters to prevent voltage drop and excessive heat.
- Battery Placement: Keep batteries in a ventilated space as they can release hydrogen gas during charging. For indoor installations, consider maintenance-free batteries.
Earthing: Proper grounding is essential for safety. Ensure your inverter system has a good earth connection to prevent electrical dangers.
Maintenance Schedule
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Importance |
| Check battery water levels (for non-sealed batteries) | Monthly | Critical |
| Clean battery terminals | Quarterly | High |
| Check and tighten connections | Quarterly | High |
| Clean inverter vents and fans | Bi-annually | Medium |
| Full system inspection | Annually | High |
Safety First: Always switch off the inverter and disconnect the battery before performing any upkeep. If you’re not comfortable with electrical systems, hire an expert technician.
Integrating Solar Power with Your Inverter
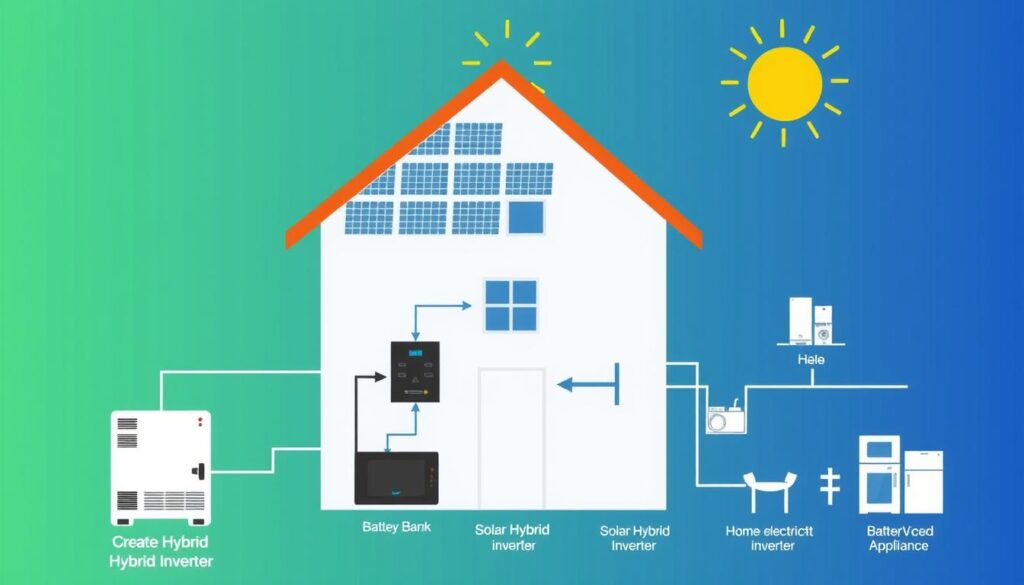
For environmentally perceptive homeowners looking to reduce electricity bills, combining solar power with your inverter system offers significant benefits. A solar hybrid inverter combines the working of a traditional inverter with a solar charge controller.
How Solar Hybrid Inverters Work
Solar hybrid inverters can draw power from multiple sources: the utility grid, batteries, and solar panels. During daylight hours, solar panels generate electricity that can either power your home directly, charge the batteries, or feed back into the grid (if net metering is available). When solar production is nor enought, the system automatically draws from batteries or the power.
Benefits of Solar Integration
Economic Benefits
- Reduced electricity bills
- Protection against rising energy costs
- Potential tax incentives and rebates
- Increased property value
Environmental Benefits
- Reduced carbon footprint
- Renewable, clean energy source
- Decreased dependence on fossil fuels
- Sustainable long-term solution
Key Considerations for Solar Hybrid Systems
When planning a solar hybrid inverter system, consider these factors:
- Solar Capacity: Calculate how many solar panels you’ll need based on your energy usage and available roof space.
- Battery Bank Size: Determine how much energy storage you need for nighttime use and backup during blackouts.
- Inverter Compatibility: Ensure your inverter is designed for solar integration with MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) technology for superior efficiency.
- Grid Connection: Check local regulations regarding grid-tied systems and net metering policies.
Recommended: Top Solar Hybrid Inverter
The Luminous Solar NXG series offers excellent performance for residential solar applications. These inverters feature MPPT technology, pure sine wave output, and smart monitoring capacities that allow you to track solar generation and utilization patterns through a mobile app.
With capacities ranging from 1100VA to 3500VA, these inverters can be scaled to meet various household needs while maximizing solar energy consumptions.
Frequently Asked Questions

Can I run my air conditioner on an inverter?
Yes, but you need a high-capability inverter particularly designed for heavy loads. For a 1.5 ton AC that utilies maximum 1800W, you’ll need an inverter rated at least 3000VA with a suitable battery bank. These specialized inverters are often marketed as “AC inverters” and require an expert installation. Keep in mind that running an AC will drain batteries rapidly, so solar integration is recommended for long-term use.
How long will my inverter battery last during a power outage?
Battery runtime depends on three factors: battery capacity (Ah rating), inverter efficiency, and the load you’re powering. As a rough estimate:
Runtime (hours) = Battery capacity (Ah) × Battery voltage × Inverter efficiency ÷ Total load (watts)
For example, a 150Ah 12V battery with 85% inverter efficiency powering a 400W load would last approximately: 150 × 12 × 0.85 ÷ 400 = 3.8 hours
What’s the difference between an inverter and a UPS?
While both provide backup power, they serve different purposes:
- Inverter: Designed for longer backup times (hours) but with a switching time of a few milliseconds. Ideal for general home backup.
- UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply): Provides instant switching (no perceptible delay) but typically for shorter durations. Primarily designed to protect sensitive electronics like computers from data loss during power fluctuations.
Some modern home inverters incorporate UPS functionality with near-instant switching times.
How do I maintain my inverter battery to maximize its lifespan?
To extend your battery life:
- For flooded batteries, check water levels monthly and top up with distilled water when needed
- Keep battery terminals clean and tight
- Avoid complete discharge; try not to let battery levels fall below 50%
- Ensure your inverter has proper charging settings for your battery type
- Keep batteries in a cool, ventilated area
- Perform an equalization charge (for flooded batteries) every 3-6 months as recommended by the manufacturer
Is a pure sine wave inverter worth the extra cost?
For most modern homes, yes. Pure sine wave inverters provide power quality identical to utility electricity, ensuring all your devices run safely and efficiently. They’re especially important if you use:
- Computers, laptops, and networking equipment
- Modern LED TVs and audio tools
- Refrigerators with digital controls
- Medical devices
- Microwave ovens and digital machinery
While changed sine wave inverters cost less initially, they may cause ruahed wear on appliances, interference in audio/video equipment, and synergy issues with sensitive electronics.
Making Your Final Decision

Choosing the best inverter for home use doesn’t have to be overwhelming. By understanding your power requirements, considering the right inverter type, and selecting appropriate battery capacity, you can ensure reliable backup power during outages.
Key Takeaways
- Calculate your total power needs before shopping for an inverter
- For most modern homes, pure sine wave inverters are the safest choice
- Match your battery capacity to your expected backup time requirements
- Consider future expansion needs, especially if you might add solar later
- Don’t compromise on quality—a reliable inverter is a long-term investment
Remember that the best inverter for your home is one that balances your specific power needs, budget constraints, and long-term goals. Whether you’re looking for basic power backup during periodic power failuers or planning a short solar solution, there’s an inverter system that’s right for you.
Ready to Get Uninterrupted Power?
Our power experts can help you select the perfect inverter system based on your specific home needs.